Salivary Gland Surgery
We have 3 pairs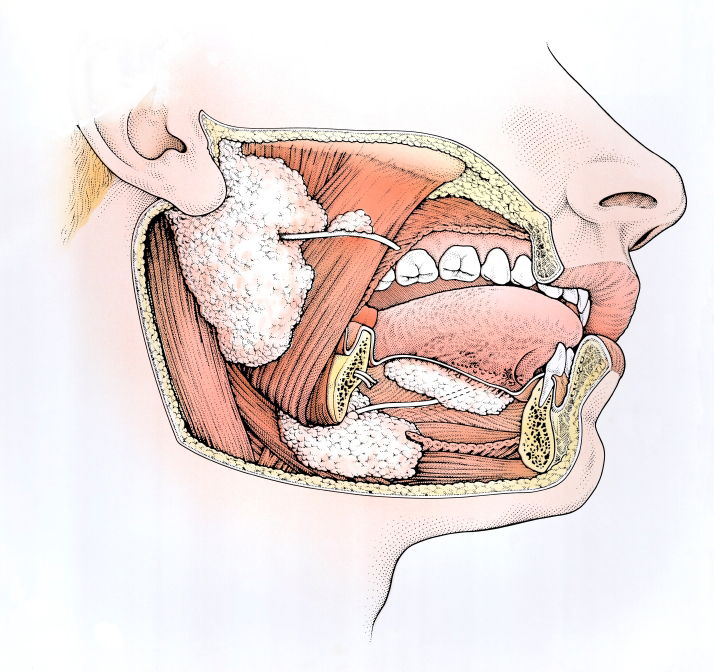 of major salivary glands: the parotid glands are in front of and below the ears, the submandibular glands are under the jaw bone, and the sublingual glands under the tongue in the mouth. There are also several hundred minor salivary glands throughout the mouth and throat. Examples of these minor glands can be felt as the small lumps inside the lower lip that can be felt with the tongue.
of major salivary glands: the parotid glands are in front of and below the ears, the submandibular glands are under the jaw bone, and the sublingual glands under the tongue in the mouth. There are also several hundred minor salivary glands throughout the mouth and throat. Examples of these minor glands can be felt as the small lumps inside the lower lip that can be felt with the tongue.
Any of these glands can develop tumors. Most of those that happen in the parotid glands are benign (80%). Cancers can be low grade that grow slowly and are less likely to spread to lymph nodes in the neck. But they can also be high grade, grow quickly and spread readily to the neck nodes. These can also be quite painful. Surgery is usually recommended for any tumor for 2 reasons: the most common benign tumor, called a pleomorphic adenoma, can become a cancer, and as tumors get bigger risks of surgery increase. The surgery is called a parotidectomy. The incision is in front of the ear, curves below the ear and then extends into the neck. After surgery, a drain is placed and patients stay overnight in the hospital. The main risks are bleeding and infection (as with any surgery), damage to the facial nerve that may paralyze areas of the face, loss of tissue volume in front of the ear, sweating of the cheek with eating (Frey’s syndrome), numbness of the ear and cheek, scar, and risks of general anesthesia. Treatment for cancer may require removal of lymph nodes from the neck and/or radiation therapy.
The main reason for removal of the submandibular glands is infection or chronic pain. Fifty percent of tumors of the submandibular glands can be malignant. Surgery for removal of these glands requires a 4-5 cm incision under the jaw. The risks include damage to the marginal mandibular nerve causing paralysis to the lower lip, numbness or loss of taste to the side of the tongue, and scar. Sometimes a drain is place, and some patients may need to stay the night in the hospital.
The sublingual glands rarely need to be removed. Unfortunately, 80% of the tumors that develop are malignant. Amore common reason for removal is a ranula, which is a collection of mucous caused by a blockage of the duct. A ranula can extend from the bottom of the mouth down into the neck. The sublingual glands are removed from the under the tongue.





